The following fungal infections (mycoses) can cause pneumonia (lung infection) and the infection can disseminate (spread). In immunocompromised people (ex. cancer treated patients, HIV patients, etc.), fungal infection will lead to systemic disease. Systemic mycosis infection can mimic tuberculosis symptoms like fever, chills, nights sweats, and weight loss.
In immunocompetent people (people with normal immunity), the fungal infection will lead to just lung disease (local infection).
These fungi are di-morphic, which means they can be in the form of mold or yeast. They are mold in the cold (20°C) and yeast in the heat (37°C). The exception is coccidioidomycosis, which is a spherule and not at yeast.
These fungi are di-morphic, which means they can be in the form of mold or yeast. They are mold in the cold (20°C) and yeast in the heat (37°C). The exception is coccidioidomycosis, which is a spherule and not at yeast.
Histoplasmosis
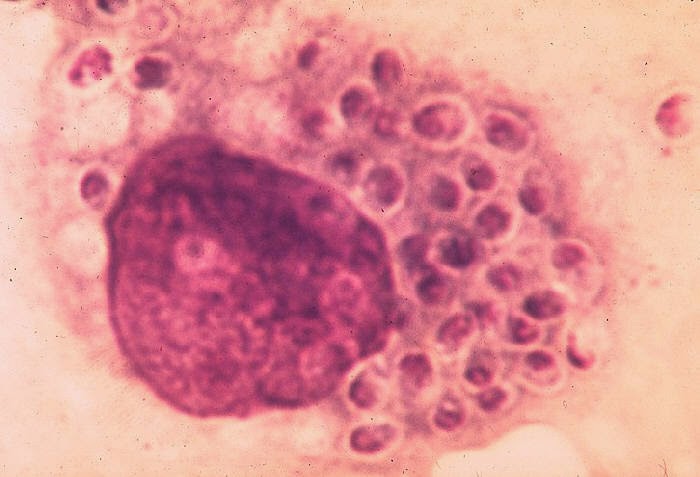 It's most common in the southeastern, mid-Atlantic, and central United States; such as the Mississippi and Ohio river valleys. It can cause an acute pneumonia, which presents as cough, fever, and malaise. Chest X-ray will show hilar adnopathy and may demonstrate areas of pneumonia. Disseminated histoplasmosis are more common in HIV patients.
It's most common in the southeastern, mid-Atlantic, and central United States; such as the Mississippi and Ohio river valleys. It can cause an acute pneumonia, which presents as cough, fever, and malaise. Chest X-ray will show hilar adnopathy and may demonstrate areas of pneumonia. Disseminated histoplasmosis are more common in HIV patients.
Labs: Microscopy will show macrophage filled with Histoplasma. Can present as coin lesions that is calcified on chest x-ray.
Key Scenario: Found in soil and droppings of birds bats so, cave exploration and cleaning bird coups is associated with the fungus. Also, doing activities that disrupt soil.
Blastomycosis

It's endemic in the south-central and north-central United States. It affects the lungs, skin, bnes, joints, and protaste. Infection in immunocompromised hosts is uncommon. Primary pulmonary infection may be asymptomatic or present with flu-like symptoms. Forms granulomatous nodules.
Labs: Microscopy will show broad-based budding; same size as RBCs. Diagnosis is made by use of potassium hydroxide (KOH) prep to reveal big broad-based budding in sputum and tissues. The organism will show thick double refractive walls around it.
Coccidioidomycosis
 It's endemic in the southwestern United States, as well Central America and South America. Primary pulmonary infection has a non-speicif features, such as fever, fatigue, dry cough, weight loss, and pleuritic chest pain. It can spread to bones as skin; cutaneous findings, such as erythema multiforme and erythema nodosum, as well as arthlagias, are common.
It's endemic in the southwestern United States, as well Central America and South America. Primary pulmonary infection has a non-speicif features, such as fever, fatigue, dry cough, weight loss, and pleuritic chest pain. It can spread to bones as skin; cutaneous findings, such as erythema multiforme and erythema nodosum, as well as arthlagias, are common.
Labs: Microscopy will show spherules filled with endospores.
Key Scenario: Patient gets infected after and earthquake, because the spherules in dust are thrown up in the air.
 |
| Image Source: Medscape |
Rx: Treated with fluconazole or ketoconazole for local infections. Amphotericin B for systemic infections.
0 comments:
Post a Comment